Photo by Dr. Haus
Anti-Diuretic Hormone
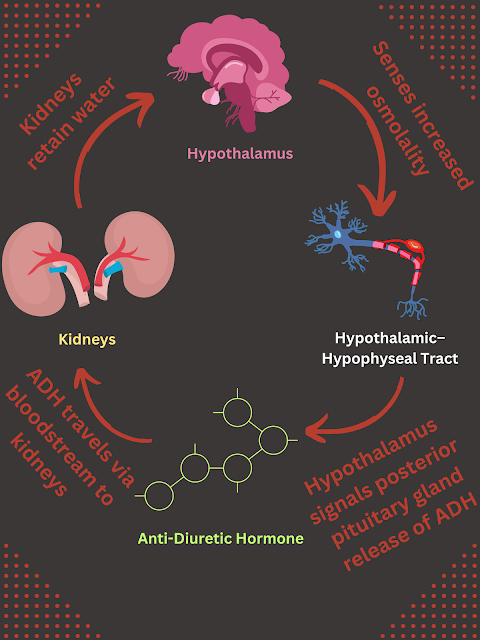
Anti-Diuretic Hormone, also called ADH or vasopressin, is a hormone that is produced in the hypothalamus and released by the posterior pituitary gland. ADH causes the kidneys to reabsorb more water thus decreasing the amount of water lost in the urine and to create a more concentrated urine.
The steps of the release of ADH is written out below and followed by an infographic:
- The hypothalamus senses increased osmolarity of the bloodstream (increased concentration of solutes)
- The osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus shrink (due to a higher osmolarity in the bloodstream versus inside these cells)
- The hypothalamus sends an electric signal via the neurons to the poster pituitary gland to release ADH
- The ADH enters the bloodstream and arrives at the kidneys
- The kidneys increase the number of aquaporins in the distal tubules and collecting ducts
- More water is reabsorbed into the body and less water is urinated out
Why is ADH Important?
ADH is extremely important because it allows the body to have the correct amount of water in the body. Water is the basis of life and if there is not enough water in the body the body will not be able to survive very long.
As an aside, alcohol and caffeine are two substances that block the release of ADH from the posterior pituitary gland. Due to this, the kidneys are not able to reabsorb water into the bloodstream which causes increased urination of very dilute urine.
Think about the last time you had an adult beverage or drank tea/coffee. Did you have to pee shortly after? Was your urine very light in color? You can thank the blocking of the release of ADH for that change. Cheers!



No comments:
Post a Comment